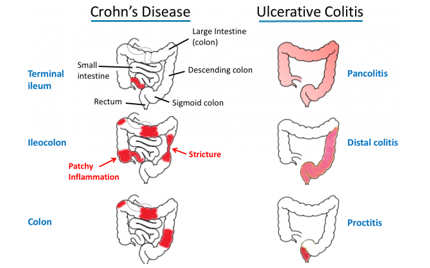
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a hard-to-treat, chronic, autoimmune condition that affects approximately 5 million people worldwide, including one million people in the U.S., with 70,000 newly diagnosed cases each year. Principal types of the disease include: Crohn’s Disease (CD) and Ulcerative Colitis (UC), with Ulcerative Proctitis (UP) and Ulcerative Proctosigmoiditis (UPS) as subcategories.
Main gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms include: abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, severe internal abdominal pain, pelvic cramps, muscle spasms and weight loss. Living with IBD is difficult as recurrence is frequent, contributing to inpatient IBD treatment costs (recently on the rise). The disease, which has been termed a "slow-motion epidemic," also is associated with an increased risk of co-morbidities.
Medications for IBD treatment include: aminosalicylates, corticosteroids, immune modifiers, antibiotics and anti-TNF agents (or biologics), which have high initial treatment failure rates and loss-of-response rates (up to 1/3 of patients for each). Treatment non-adherence occurs in up to 50 percent of IBD patients.
The total annual financial burden of IBD, in the U.S., is estimated to range between $14.6 and $31.6 billion.
Brilacidin for IBD
Brilacidin, the Company’s novel immunomodulatory drug candidate (a defensin-mimetic), is being tested (while administered as a retention enema) in a Proof-of-Concept, Phase 2 open-label, dose-escalated study in UP/UPS. Efficacy, safety and pharmacodynamics (PK) is being assessed in three dosing regimens—Cohort A (50 mg), Cohort B (100 mg), and Cohort C (200 mg). For all patients, endoscopic evaluation of the rectum and mucosa up to 40 cm from the anal verge will be performed at screening and at the end of treatment (Day 42, ± 3 days), with the scoring performed by trial investigators and independent gastroenterologists. The Primary Efficacy Endpoint of the Brilacidin UP/UPS trial uses Modified Mayo Disease Activity Index (MMDAI) scoring, a common measurement tool in managing UC preferred by many IBD specialists, to determine Clinical Remission at Day 42. Secondary Efficacy Endpoints include: change in MMDAI score, both Full and Partial, and; change in patient Quality of Life as assessed by the Short Inflammatory Bowel Disease Questionnaire (SIBDQ).
Previously released interim results, through the first two cohorts (12 patients), reinforce Brilacidin’s potential as a promising novel treatment for patients suffering from a range of debilitating inflammatory bowel conditions. Planning is underway for additional formulations—foam, gel/lotion—which should facilitate Brilacidin’s adhesion to the mucosal lining of the GI tract and may lead to even greater efficacy.
The Company anticipates treatment of the final Brilacidin UP/UPS cohort to be completed in June, with topline interim results across all cohorts to be presented at Drug Discovery & Therapy World Congress in Boston, MA July 10-13, 2017.