As announced today, Innovation Pharma’s computationally-designed (pdf) de novo defensin-mimetic COVID-19 drug candidate, Brilacidin, was ranked in the top three percent of compounds predicted to be most effective against SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus responsible for COVID-19.
Out of 1,482 compounds screened, the predictive model identified 47 compounds, which included Brilacidin, as the most promising potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. The ranking was based on a compound’s likely ability, due to physicochemical properties, to bind to three key coronavirus proteins (PL-Pro, 3CL-Pro, Spike Protein), thus inhibiting replication.
A separate independent peer-reviewed in silico screening study of 11,552 compounds, as previously released, also identified Brilacidin as one of the most promising potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2, likely able to interfere with the novel coronavirus’s main protease.
These predictive modeling studies complement a growing body of antiviral data—notably, positive pre-clinical Brilacidin testing results against SARS-CoV-2 in multiple cell lines and in different coronavirus strains—that support Brilacidin’s treatment potential in COVID-19.
Innovation Pharma has initiated a randomized, placebo-controlled Phase 2 trial of Brilacidin for treatment of moderate-to-severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients (see NCT04784897).
Brilacidin has received FDA Fast Track designation for the potential treatment of COVID-19.
For additional background on Brilacidin’s antiviral properties, refer to the peer-reviewed article recently published in the journal Viruses. Also see Salata C et al for a review of the antiviral activity and therapeutic potential of cationic amphiphilic drugs, like Brilacidin.
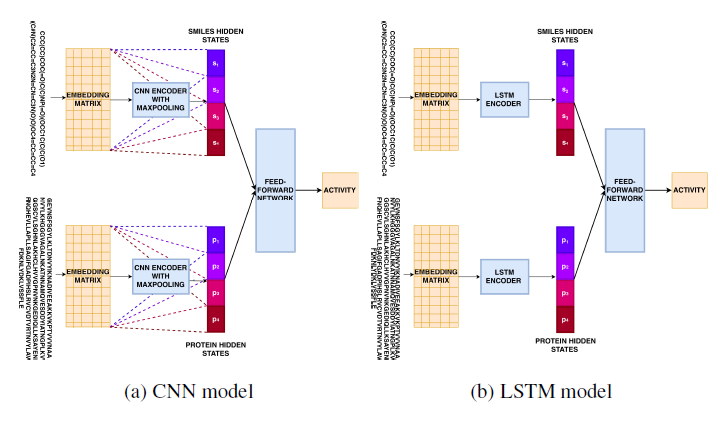
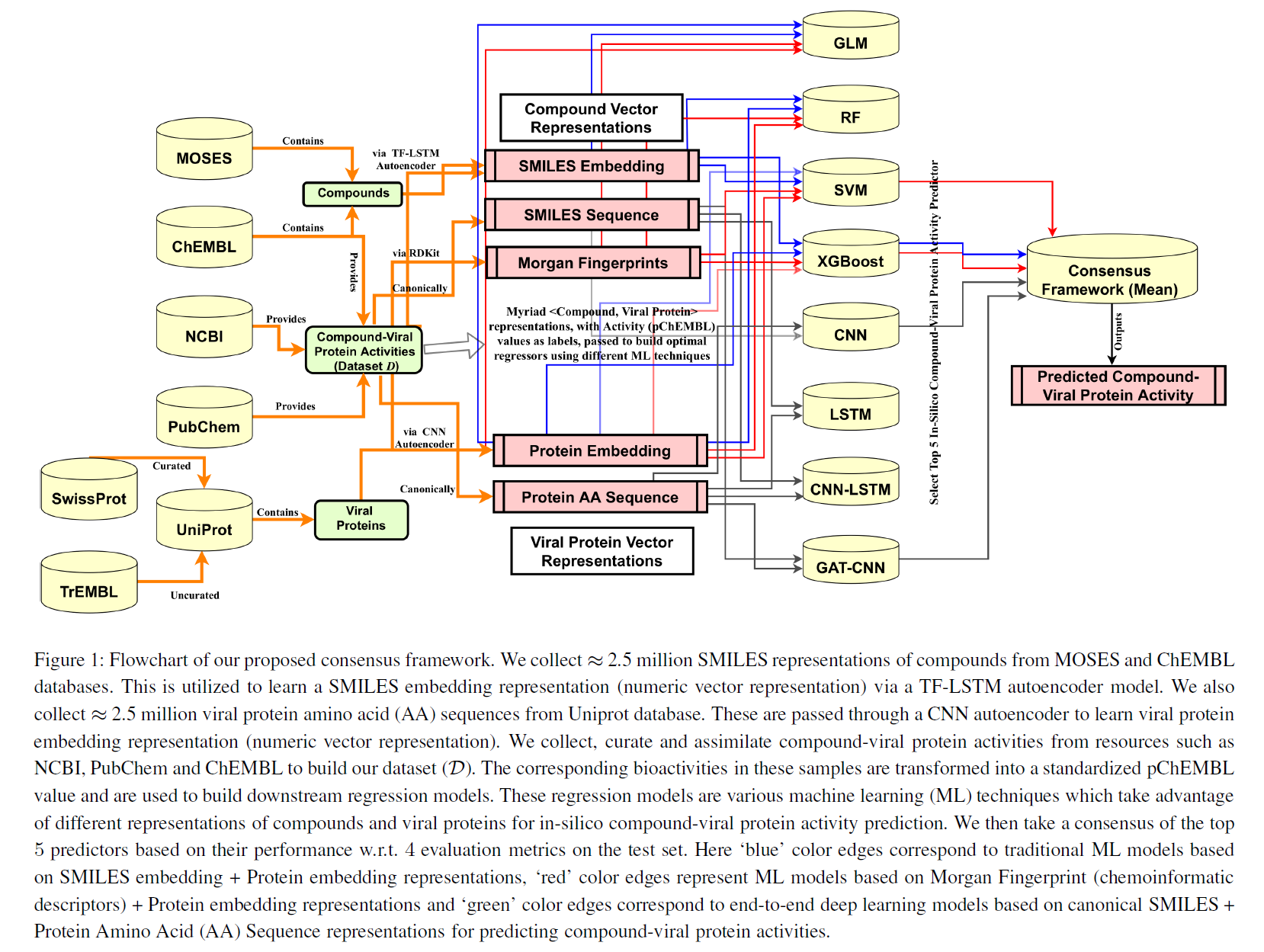
Source: Mall, R.; Elbasir, A.; Almeer, H.; et al (2021). A Modelling Framework for Embedding-based Predictions for Compound-Viral Protein Activity. Bioinformatics, btab130, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab130 (Published: 26 February 2021)